Revenue Cycle Management Healthcare. A Comprehensive Guide
In the healthcare industry, revenue cycle management healthcare is the process of overseeing the financial facets of patient care from the time of registration to payment collection and beyond. Medical coding, insurance verification, patient registration, billing, and payment collection are some of the interconnected procedures that are involved. Healthcare organizations’ financial health is greatly influenced by revenue cycle management healthcare. It is critical to ensure that providers are reimbursed for their services in a timely and accurate manner.
Significance of RCM in Healthcare Practices:
Due to staff overload and limited resources, inefficiencies in processes might easily go unnoticed unless they are investigated and reported. Further impediments to the identification of such efficiencies may include the departmental barriers effect and a general lack of responsibility.
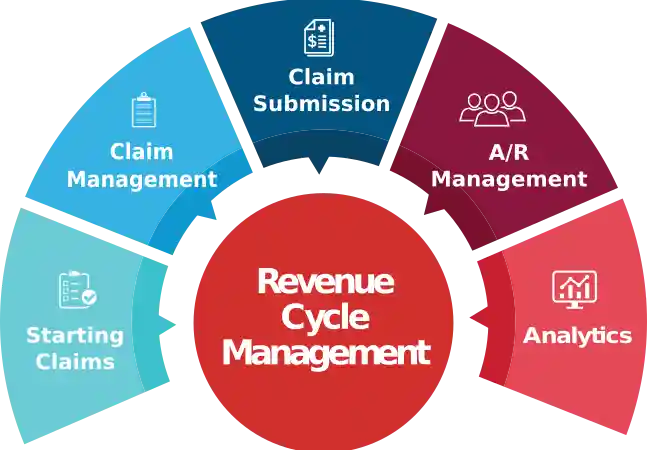
Steps in Revenue Cycle Management:
A revenue cycle consists of 16 steps however, the particular processes may differ slightly based on the policies of a particular healthcare facility.
1) Scheduling Appointments:
Patient appointment scheduling is the first step in the revenue cycle management process. This includes gathering their name, date of birth, insurance information, and purpose for visit, among other personal and medical data.
2) Patient Registration:
The patient has to fill out registration forms with their personal and health information after making an appointment. Accurate billing and eligibility and benefit verification are also made possible with the use of this data.
3) Insurance and Eligibility Verification:
In order to determine their financial responsibilities, healthcare professionals must confirm the insurance coverage and benefits of their patients. This means looking up copays, deductibles, and other payment information on the patient’s insurance plan.
4) Utilization analysis:
A utilization analysis verifies that the medical treatments patients receive are both medically required and compliant with insurance requirements. The purpose of this review is to stop needless procedures that could lead to claim rejections or nonpayment.
5) Authorization and Referral:
Before accessing specialty care or services, several insurance plans require a recommendation or authorization from an insurance company or primary care physician.
6) Description of Charges:
Healthcare providers are required to give a full explanation of the charges collected during a patient’s visit. This covers any medical equipment used, recommended drugs, and services provided.
7) Billing and Coding:
Assigning the proper codes to medical procedures and services guarantees that the claim appropriately represents the treatment rendered. This process is known as coding and billing. Inaccurate payments or claim rejections are prevented by this procedure.
8) Charge Entry:
Healthcare providers post costs to the patient’s account after charging the insurance company. By taking this step, the patient’s account balance is guaranteed to be current.
9) Submits Claim:
The healthcare provider submits the claim with the insurance company for payment when the costs posted.
10) Denials by Clearinghouse:
Insurance companies can reject claims because of inaccurate coding or missing information. Clearinghouses used by healthcare providers to monitor and handle claim denials.
11) Post payments:
The patient’s account credited with the payment once the insurance company approved the claim. This process guarantees that the amount received reflected in the patient’s account balance.
12) Denial management:
Resolving any possible claim denials or problems is the responsibility of denial management. In order to resubmit the claim for payment, healthcare providers must determine the reason for the denial and take the appropriate action.
13) Additional filing:
The medical professional might have to submit a second claim to the patient’s secondary insurance company if the first one rejected.
14) Accounts receivable:
Accounts receivable management include keeping track of the patient’s outstanding balances. This procedure guarantees the accuracy of the patient’s account and the payment of the healthcare provider for the services provided.
15) Appeals:
Healthcare providers have the right to file an appeal if a claim rejected. In order to verify payment and support the claim, more paperwork or information must submitted during the appeals process.
16) Collection of Patient Billing:
The collection of patient bills is the last phase in the revenue cycle management process. In this step, patients will receive statements or bills for any unpaid amounts. In order to get payment, the healthcare provider could also collaborate with a collection agency.
Benefits of Revenue Cycle Management in healthcare industry:
1) Better Cash Flow:
Practices have better overall cash flow when they short the time it takes to get pay for their services.
2) Revenue Growth:
Through precise and quick claim processing, practices lower the number of claim denials and increase the possibility that services will paid in full.
3) Improved Patient Experience:
Providers can give patients a better experience by cutting down on billing errors and expediting the payment procedure.
4) Higher Level of Compliance:
Medical practices can lower their risk of financial penalties and legal concerns by making sure they remain compliant with healthcare standards.
Conclusion:
It is more important than ever for practices to examine their requirement for robust and dependable revenue cycle management services. The Medicator’s offers flexible RCM services to meet a range of requirements. Speak with us right now to find out how we can assist.