Lithium chloride, or LiCl, is a valuable and adaptable chemical molecule that is used in a wide range of sectors, including pharmaceuticals and energy storage. Its unique properties make it indispensable in multiple applications, enhancing technologies and improving human life. This article explores the diverse lithium chloride uses, highlighting its significance in batteries, pharmaceuticals, and other key areas.
Lithium Chloride In Battery Technology
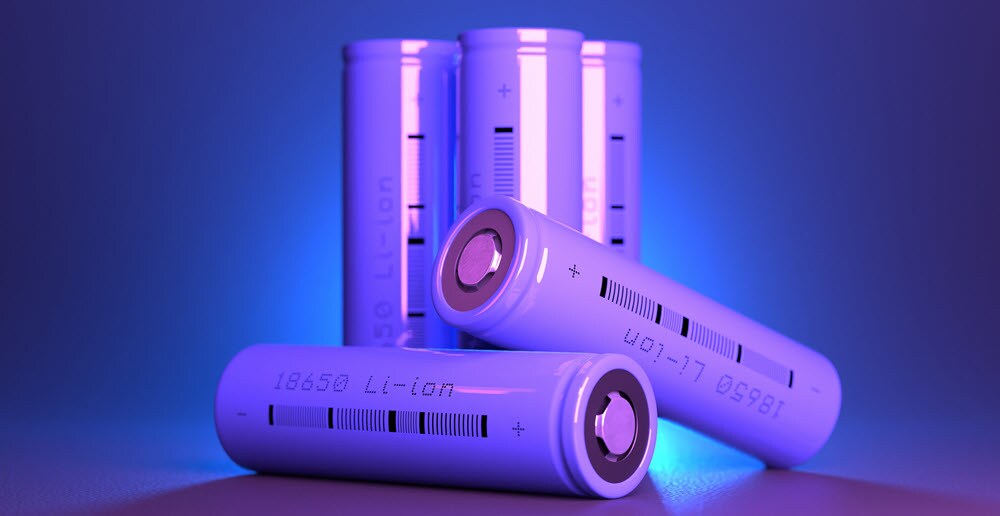
One of the most prominent uses of lithium chloride is in the production of lithium-ion batteries. Because of these batteries’ great energy density, extended lifespan, and lightweight design, they are frequently found in portable devices, electric cars, and renewable energy storage systems. Lithium chloride acts as a precursor in the synthesis of lithium metal, which is a critical component of lithium-ion batteries.
In battery technology, lithium chloride is used to produce lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), an essential electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries. Energy may be stored and released because of the electrolyte’s ability to promote the flow of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. The efficiency and performance of lithium-ion batteries are significantly enhanced by the presence of high-purity lithium chloride, ensuring reliable power for a wide range of applications.
Pharmaceuticals And Medical Applications
Lithium chloride also plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Patients with bipolar disorder frequently take lithium salts, such as lithium chloride, as mood stabilisers to control and prevent manic and depressive episodes. The therapeutic effects of lithium are believed to result from its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity and enhance neuroplasticity, thereby stabilising mood and reducing the severity of mood swings.
Additionally, lithium chloride has been investigated for its potential neuroprotective properties. Lithium may aid in shielding neurones from harm and encouraging the formation of new brain connections, according to research, which may have consequences for the treatment of neurodegenerative illnesses, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. Although further investigation is necessary to completely comprehend these consequences, lithium chloride shows promise for therapeutic use in neurology.
Industrial And Chemical Applications
Beyond its roles in batteries and pharmaceuticals, lithium chloride is widely used in various industrial and chemical processes. One of its primary applications is as a desiccant or drying agent. Lithium chloride’s hygroscopic nature allows it to absorb moisture from the air, making it useful in controlling humidity levels in packaging, air conditioning systems, and laboratory environments. Its effectiveness in moisture control helps prevent corrosion, mould growth, and other moisture-related issues.
In the field of synthetic chemistry, lithium chloride is utilised as a reagent and catalyst in various chemical reactions. It is commonly employed in the synthesis of organic compounds, where it can influence reaction pathways and improve yields. Lithium chloride’s ability to stabilise reaction intermediates and promote specific chemical transformations makes it a valuable tool for chemists in developing new materials and pharmaceuticals.
Water Treatment And Environmental Applications
Lithium chloride also finds application in water treatment and environmental monitoring. It is used in the production of lithium-ion exchange membranes, which are essential components in water desalination and purification systems. These membranes help remove contaminants and salts from water, making it suitable for drinking and irrigation. Lithium-ion exchange membranes’ longevity and effectiveness support the sustainability of water resources, particularly in areas where water is scarce.
Furthermore, lithium chloride is utilised in the development of humidity sensors and environmental monitoring devices. These sensors rely on the hygroscopic properties of lithium chloride to detect and measure moisture levels in the air. Accurate humidity monitoring is crucial in various industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and climate research, where maintaining optimal humidity levels is essential for quality control and environmental protection.
Conclusion
Lithium chloride’s diverse applications in battery technology, pharmaceuticals, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring underscore its importance in modern society. Because of its special chemical characteristics, it is a valuable and adaptable substance that is advancing environmental sustainability, medical treatments, and energy storage. As research continues to uncover new uses and refine existing applications, lithium chloride will remain a critical component in shaping the future of technology and improving human well-being.